Ovarian cancer is a rapid growth of cells that forms in the ovaries or changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell the cell what to do. The changes tell the cells to grow and multiply quickly, creating cancer cells' mass (tumor). The cancer cells continue living when healthy cells would die. They can invade nearby tissues and break off from an initial tumor to spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body. Ovarian cancer is now the fifth most common cause of cancer-related death among females in the united states of America and third in the world, according to the American cancer society (ASC).
In the early stages of ovarian cancer, which starts in the epithelium or outer lining of the ovary, there may be no or some symptoms which can be easily attributed to other ailments such as constipation or temporary bladder problem, However after sometimes some, there are would-be some persistent symptoms such as:
Symptoms
- Bloating
- Pains in your pelvic region
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue
- Frequent urination
- Weight loss
- Unexpected vaginal discharge or Bleeding
- Pain during sex
- Back pain
However, women should be noted that even though these are signs of ovarian cancer, there can be some other causes because the signs of ovarian cancer are common and somewhat vague. The symptoms can change if cancer spreads to other parts of the body.
So it's advisable to visit your doctor once your notice any of these signs.
Note: Symptoms that last more than a couple of weeks are key to spotting ovarian cancer. Only about 15% of ovarian cancer is diagnosed in the early stages. Many women don't notice problems until a tumor is more advanced.
Causes and Risk factors
- Family History: If you have blood relatives who have been diagnosed with ovarian cancer, you may have an increased risk of the disease.
- Gene: A small percentage of ovarian cancers are caused by genes changes you inherit from your parents. The genes that increase the risk of ovarian cancer include BRCA1 and BRCA2. These genes also increase the risk of breast cancer. Several other gene changes are known to increase the risk of ovarian cancer, including gene changes associated with Lynch syndrome and the genes BRIP1, RAD51C, and RAD51D. Undergoing genetic screening for mutations in the BRCA gene may help determine if someone has a higher risk of ovarian cancer.
- Reproductive History: Having had one or more full-term pregnancies is associated with a lower risk of ovarian cancer. The more pregnancies a woman has, the lower the risk. Breastfeeding may also lower the risk. However, having children later in life (after age 35) or never having children is a higher risk.
- Hormonal Therapy: Taking hormone replacement therapy to control menopause signs and symptoms may increase the risk of ovarian cancer. The longer a person uses HRT, the higher the risk. However, the risk appears to fall after treatment stops.
- Age: The risk of ovarian cancer increases as you age. It's most often diagnosed in older adults. Around 50% of ovarian cancer cases occur after 63 years.
- Obesity or overweight: Ovarian cancer is more common in people with a body mass index (BMI) of over 30.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV): Scientists have found links between the human papillomavirus (HPV) and various cancers, including tonsil and cervical cancer. In 2013, the authors of a meta-analysis reported finding a high rate of HPV among people with ovarian cancer. However, they could not confirm that HPV causes it, and they called for further research.
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis is an often painful disorder in which tissue similar to the tissue that lines the inside of your uterus grows outside your uterus.
- Early menstruation or menopause: Beginning menstruation at an early age or starting menopause at a later age may increase the risk of ovarian cancer.
Types
There are over 30 types of ovarian cancer, depending on the type of cell in which they start.
There are three common cell types:
- Epithelial ovarian cancer. This type occurs in the lining of the surface of the ovary is the most common. It includes several subtypes, including serous carcinoma and mucinous carcinoma.
- Stromal tumors. These rare tumors are usually diagnosed earlier than other ovarian cancers. It is caused by the stromal cells, which release hormones and link up the structures of the ovaries.
- Germ cell tumors. These rare ovarian cancers tend to occur at a younger age.
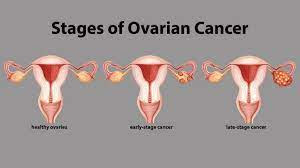
Stages
If a healthcare professional diagnoses ovarian cancer, they will need to determine the stage and grade to decide on a treatment plan.
The stage refers to how far cancer has spread. For example:
- Localized: Cancer cells affect only the ovaries or fallopian tubes and have not spread elsewhere.
- Regional: Cancer has spread to nearby organs, such as the uterus.
- Distant: Cancer is present elsewhere in the body. It now affects other organs, such as the lungs or liver.
The grade, meanwhile, refers to how abnormal the cancer cells appear.
Getting an early diagnosis usually means that treatment can be more effective. However, other factors can affect this.
These factors include the person's age and overall health and the type or grade of the cancer cell, as some types are more aggressive than others.
Diagnosis
Constant update information with your doctor to check when there is a possibility of ovarian cancer; some questions may be asked by a doctor, such as :
- ask the person about their personal and family medical history
- carry out a pelvic examination
They may also recommend:
Blood tests: These tests will check for high levels of a marker called CA-125.
Imaging tests: Examples include transvaginal ultrasound, an MRI scan, or a CT scan.
Laparoscopy: A healthcare professional will insert a thin tube with a camera attached through a small hole in the abdomen to see the ovaries and perhaps take a tissue sample for a biopsy.
Biopsy: This involves the microscopic examination of a tissue sample.
Only a biopsy can confirm that a person has cancer. A healthcare professional may do this as part of the initial assessment or following surgery to remove a tumor.
Treatment
Treatment will depend on many factors, including:
- the type, stage, and grade of the cancer
- the individual's age and overall health
- their personal preferences
- accessibility and affordability of treatment
Surgery: The choice will depend on the type of cancer and how far it has spread. Surgical options include a hysterectomy, removing one or both ovaries, and removing affected lymph nodes. A doctor will discuss suitable options with the individual.
Chemotherapy: These drugs aim to kill cancer cells. If a person takes chemotherapy drugs by mouth or as an injection or infusion, they will affect the whole body. Another option is intraperitoneal chemotherapy. In this case, a tube delivers the drug directly to the body area affected by cancer. Chemotherapy can have widespread adverse effects, especially if it affects the whole body.
Targeted therapy: Some treatments target specific cells that help promote cancer growth. Examples include monoclonal antibody therapy and angiogenesis inhibitors. Targeted therapy aims to limit the adverse effects by targeting specific functions.
Radiation therapy: This technique uses X-rays to kill cancer cells. One way to do this is by introducing a radioactive liquid into the peritoneum. This therapy may help people with advanced ovarian cancer.
Immunotherapy (biotherapy): This aims to boost the immune system's ability to defend the body against cancer. Vaccine therapy involves injecting substances that will find and kill a tumor. It may help people with advanced ovarian cancer.
Some of these are relatively new types of treatment. Some people may opt to join a clinical trial that can access some of the newest approaches.
Prevention
Symptoms and causes
There's no sure way to prevent ovarian cancer. But there may be ways to reduce your risk:
- Consider taking birth control pills. Ask your doctor whether birth control pills (oral contraceptives) may be right. Taking birth control pills reduces the risk of ovarian cancer. But these medications do have risks, so discuss whether the benefits outweigh those risks based on your situation.
- Discuss your risk factors with your doctor. If you have a family history of breast and ovarian cancers, bring this up with your doctor. Your doctor can determine what this may mean for your own risk of cancer. The doctor may refer you to a genetic counselor who can help you decide whether genetic testing may be right for you. If you're found to have a gene change that increases your risk of ovarian cancer, you may consider surgery to remove your ovaries to prevent cancer.
- Gynecological surgery: Having surgery to remove the uterus, called a hysterectomy, may reduce the risk of ovarian cancer by one-third.
Conclusion
All types of ovarian cancer are treatable if a person receives a diagnosis in the early stages. Some types are also highly treatable in the later stages.
When considering survival statistics for ovarian cancer, it is also worth noting that medical advances have improved the outlook over the past 20 years.
Nevertheless, attending a regular screening and seeking help if any symptoms appear can often lead to an early diagnosis, increasing the chance of receiving effective treatment.